What is Data Governance? The Ultimate Guide
What is Data Governance?
The Ultimate Guide
In today’s digital world, businesses are embracing digital transformation to change the way they provide services to the customers, and the underlying promise of digital transformation is data.
The data plays the key role, empowering the new business models, improving customer experiences, and accelerating business intelligence.
What is Data Governance?
Data Governance refers to the set of processes and procedures where organisations used to handle, utilize, and protect their data. Once what data means is defined, you can formulate ways to use your data in different ways that advance your business. Data governance is of paramount importance to any business.
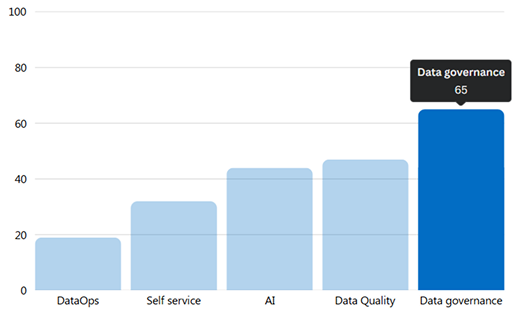
According to the Gartner Data & Analytics Summit held in Orlando, Florida, over 65% of data leaders highlighted data governance as their main focus, followed by data quality (47%), AI (44%), self-service (32%), and DataOps (19%).
Data Governance is the top priority for 65% of data leaders
- Data quality (47%)
- AI (44%)
- Self service (32%)
- DataOps (19%)
Source: Humans of data
The Importance of Data Governance
As per Gartner reports, 80% of digital organisations will fail because they don’t take a modern approach to data governance. Data governance helps to make sure that data is usable, accessible, consistent and secure. The effective data governance always leads to better data analytics, improved decision-making, and enhanced operations support.
Data governance can help organisations to avoid data inconsistencies or errors in data, which results in integrity issues, poor decision-making, and other organisational problems.
The data governance also plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance, ensuring that the businesses are compliant with the regulatory requirements. This is necessary in industries such as banking and healthcare, where data is subject to strict privacy and security regulations.
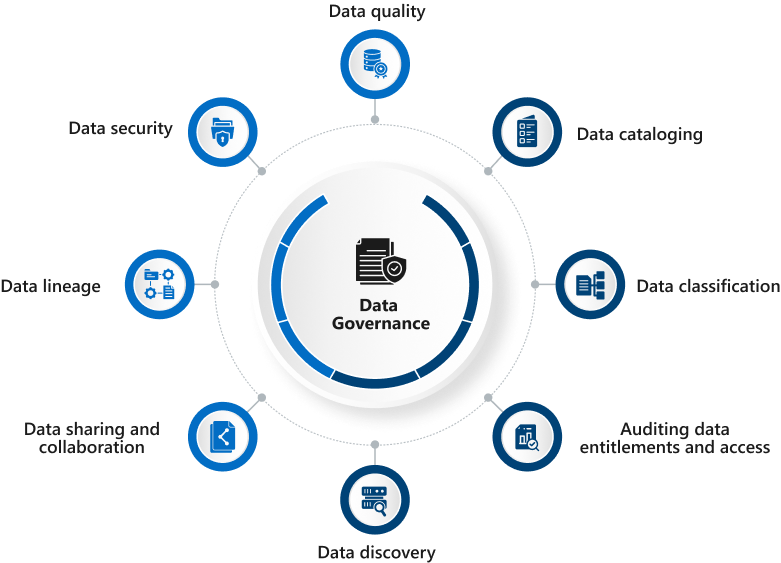
Key Components of a Data Governance Strategy
To create a solid Data Governance strategy, the below critical components are required.
- Data Cataloguing
- Data Classification
- Auditing data entitlements and access
- Data Discovery
- Data Sharing & Collaboration
- Data Lineage
- Data Security
- Data Quality
- Compliance and Privacy
Data Cataloguing
Effective data governance requires data knowledge that exists within an organisation. The Data Catalogue comes in, where it provides a centralized metadata repository for an organisation’s data assets. Implementing a data catalogue into a governance program enables organisations to enhance their data management, improve collaboration, reduce redundancy, and ensure proper access controls.
Data Classification
Data classification is a key part of data governance which involves organizing and classifying data based on its sensitivity, value, and criticality. Data Classification enables organisations to identify and categorize data based on its risk level and importance thus allowing the organisations to apply appropriate security measures and policies.
Auditing data entitlements and access
One of the key aspects of data governance is data access auditing and with a thorough understanding of who has access to what data and with the track of recent access, organisations can easily identify overentitled users or groups and minimise the risk of data misuse. Data breaches and regulatory noncompliance may occur when a proper audit mechanism is not in place and when organisations are not fully aware of their risk surface area.
Data Discovery
With the rise of modern data assets like dashboards, machine learning models, queries, libraries, and notebooks, data discovery has become a key pillar of data governance strategy. It helps organisations and enables data teams to locate data assets easily across the organization, collaborate on various projects, and innovate quickly and efficiently.
Data Sharing & Collaboration
As the data exchange occurs among organisations with internal teams, external partners, and customers across multiple clouds businesses must exchange the data securely while maintaining control and visibility over how their secured information is used. To meet their data-driven innovation needs, organizations need to invest in open-format, interoperable, and multi-cloud data-sharing technologies.
Data Lineage
Data lineage is a powerful tool which helps to capture relevant metadata and events throughout the data’s lifecycle, providing a holistic view of how data flows across an organisation’s data estate.
Data Security
If the organisation lacks adequate security measures, the business is being exposed to cyberattacks leading to potential loss of customer trust, regulatory fines, and significant financial and reputational damage.
Data Quality
With incorrect data or data quality, the risk of making decisions based on outdated or incorrect information is higher. It can lead to lost revenue, ineffective marketing strategies, and poor customer experiences. Thus, the accurate and relevant data will help you improve customer targeting, help with personalisation, and help with satisfaction.
Compliance and Privacy
Strictly adhering to data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA helps your organisation to avoid hefty fines and improves customer trust by highlighting your commitment to privacy and ethical data use. It is also necessary for an organisation to stay up to date on new security compliance standards as they are released.
Difference between Data Management and Data Governance
| Aspects | Data Management | Data Governance |
| Definition | The technical implementation of managing data throughout its lifecycle. | The strategic framework of policies, roles, and standards to ensure data is used responsibly and aligns with business goals. |
| Focus | Operational tasks: data ingestion, integration, storage, transformation, backup, retrieval, and archiving. | Policy-making: data quality, ownership, compliance, privacy, security, and risk management. |
| Objective | Efficient and reliable handling of data. | Ensuring data is trustworthy, secure, and aligned with regulatory and business requirements. |
| Responsibility | IT and Data Operations teams. | Business stakeholders, compliance officers, data stewards, and governance committees. |
| Key Elements | Databases, ETL tools, data warehouses, backup systems. |
Policies, standards, data stewardship, roles, and accountability. |
| Outcome | Smooth data flow and accessibility across systems. | High-quality, secure, and compliant data for informed decision-making. |
| Relation to Strategy | Executes the data strategy operationally. | Drives and shapes the organization’s long-term data strategy. |
| Risk without it | Disorganized data systems, slow processes. | Poor data quality, compliance issues, and unreliable insights. |
Difference between Data Management and Data Governance
- Data Management: The technical implementation of managing data throughout its lifecycle.
- Data Governance: The strategic framework of policies, roles, and standards to ensure data is used responsibly and aligns with business goals. ✅
- Data Management: Operational tasks: data ingestion, integration, storage, transformation, backup, retrieval, and archiving.
- Data Governance: Policy-making: data quality, ownership, compliance, privacy, security, and risk management. ✅
- Data Management: Efficient and reliable handling of data.
- Data Governance: Ensuring data is trustworthy, secure, and aligned with regulatory and business requirements. ✅
- Data Management: IT and Data Operations teams.
- Data Governance: Business stakeholders, compliance officers, data stewards, and governance committees. ✅
- Data Management: Databases, ETL tools, data warehouses, backup systems.
- Data Governance: Policies, standards, data stewardship, roles, and accountability. ✅
- Data Management: Smooth data flow and accessibility across systems.
- Data Governance: High-quality, secure, and compliant data for informed decision-making. ✅
- Data Management: Executes the data strategy operationally.
- Data Governance: Drives and shapes the organization’s long-term data strategy. ✅
- Data Management: Disorganized data systems, slow processes.
- Data Governance: Poor data quality, compliance issues, and unreliable insights. ✅
Steps for Implementing a Data Governance Framework
The initial step would be to identify the key stakeholders who are involved in the data governance process, including business leaders, data owners, and data users.
A set of policies and procedures need to be developed that highlights how data will be collected, stored, accessed, and used in an organisation.
To oversee the implementation of the data governance framework, a data governance council or committee needs to be established.
An effective data governance plan should be created that highlights the specific steps that will be taken to implement the framework, including timelines and budgets.
The data governance framework needs to be communicated with the stakeholders and provide training and support as required.
Evaluate and monitor the data governance framework effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Governance

The Global Data Governance Market is on a sharp rise!
Prioritize Stakeholder Engagement:
One of the key things is to engage stakeholders from different departments early and frequently to make sure their needs are addressed, leading to successful implementation.

$2.1 billion to $5.7 billion in 2025
That’s a 171% increase in just 5 years!

$2.1 billion to $5.7 billion in 2025
That’s a 171% increase in just 5 years!
Data Inventory and Classification
Before effectively managing the data, need to understand the data we have. Start by analysing the data inventory that involves analysing data assets within an organisation. The data can be classified based on sensitivity, importance, and usage. This set of practices allows us to prioritize the data governance efforts. Hence the critical data receives the highest level of protection and oversight.
Data Privacy and Security Policies
Data privacy and security are paramount in today’s digital landscape. Implementing robust data privacy policies and security measures protects sensitive information from breaches and unauthorized access. This process includes encrypting data, implementing access controls, and adhering to industry-specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA etc.
Data Quality Management
For effective decision-making, high-quality data is the key factor. To eliminate errors, redundancies, and inconsistencies establish data quality standards, and regularly monitor and cleanse the data. This ensures that the data remains accurate and reliable driving better business outcomes.
Data Access Control and Permissions
Control access to your data by defining user permissions and roles. Restrict data access to only those individuals who need it for their specific job roles. Implement strict authentication and authorization mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
Leverage Automation
Improve efficiency and reduce the chances of human errors by automating repetitive data governance tasks such as data quality checks and monitoring compliance.
Clear Communication Channels: Establish open and transparent communication channels to keep all the team members informed on governance principles, standards, procedures, and changes.
Implement a flexible governance framework
Implementing a flexible framework can help with the need for changes in your organisation. To incorporate this method, it is essential to map your current data ecosystem and determine how data flows and where bottlenecks might occur. Later this information can be used to develop a modular framework, and this way it is easier to stay aligned with goals and keep up with business needs.
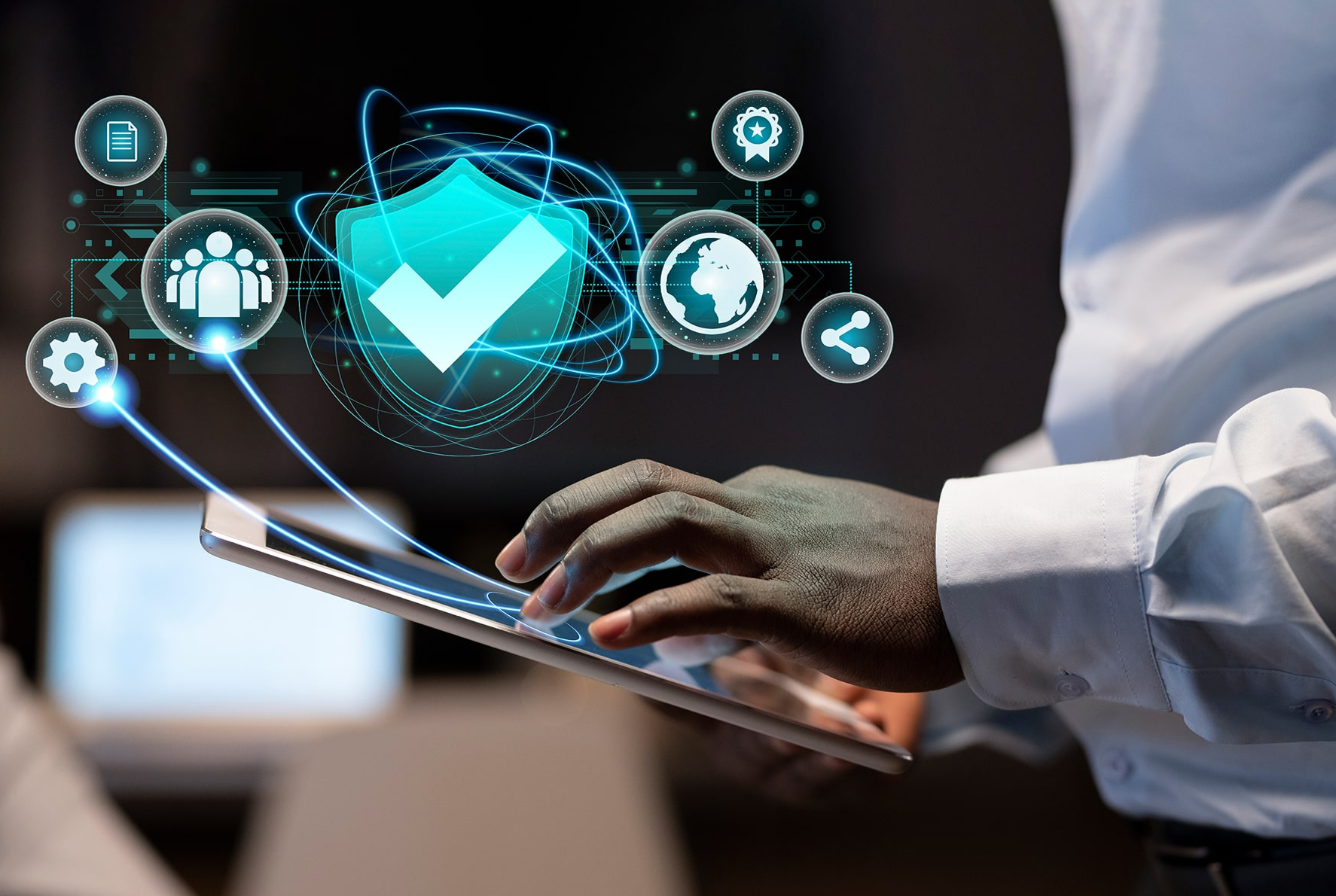

Primary Benefits of Data Governance
Effective data governance approach brings many benefits for organisations, and these can be broadly categorized as below:
High-Quality Data
Data governance ensures data accuracy, consistency, and integrity. High-quality data allows organisations to understand their customers and workflows better, which helps to optimize the overall business performance.
Improved Decision making
One of the major benefits of data governance is improving decision-making strategies. A well-governed data is complete and more identifiable, making it easier for data teams to discover useful insights. Thus, the businesses achieve their goals with high accuracy.
Improving Compliance and Reducing Risks
Adhering to regulations is crucial, especially in industries such as healthcare, banking and finance, retail, etc. Data governance ensures that all data practices comply with industry regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX. This regulatory compliance builds trust with customers by establishing a commitment to data privacy and security.
Facilitating Data Access and Integration
Data governance ensures that data is accessible and available to those who need it and when they need it. Businesses can improve operational efficiency and ensure that critical information is available for decision-making while removing barriers to data access.
Accountability and Ownership
With clearly defined data governance policies the data ownership and responsibilities are set with clarity. This clarity makes sure that every user understands their role in managing and protecting data, promoting accountability m, and eliminating the risk of errors.
Top Data Governance Trends for 2025
Cloud-based Data Governance Framework
Cloud-based data governance is emerging as a trend that is set to be critical for organisations that ensure data compliance and discovery. With businesses embracing cloud-based, distributed data architectures like data mesh, a flexible cloud-based data-governance framework helps to manage their data effectively.
Data Governance as a Service (DGaaS)
Today, data governance as a service is an emerging new trend, a cloud-based approach to data governance that leverages cloud infrastructure to offer organisations the tools, processes, and expertise required for effective data governance.
Data Democratization and Self-Service Analytics
Data democratization allows non-technical teams to use the data they want safely. This trend focuses on enabling broader data access while maintaining governance controls and ensuring data literacy across the organisation.
- Self-service data catalogs
- Governed data visualization tools
- Role-based access controls
- Data literacy programs
- Automated data discovery portals
Blockchain-based data governance
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve data security and transparency significantly. Many companies are considering it for their data management systems because it is decentralized, maintains immutable records, and enables secure information sharing while protecting privacy. This trend is expected to grow as businesses look to comply with data privacy regulations and build customer trust.
Types of Data Governance Acts
- GDPR – General Data Protection Regulation applies to any organisation processing European residents’ data, despite where the organisation is located.
- CCPA – The California Consumer Privacy Act focuses on consumer privacy rights, and CCPA will regulate data belonging to individuals that includes internet activity, cookies, IP addresses, and biometric data.
- HIPAA – The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, commonly known as HIPAA, is a series of regulatory standards that protects sensitive patient data information.
- DPDP – Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 aims to enhance privacy and data protection of digital personal data in India. It emphasizes on transparency, accountability, and individual control and sets rules for how organizations collect, process, and store personal data.
Indian Public Sectors on Data Governance
As per the study of New Qlik, 65% of India’s public sector leaders prioritise data strategy and governance. Also, the study states that Indian Chief Data Officers (CDOs) in the public sector are emphasizing the importance of data governance, security, and compliance.
While digital transformation is imperative, the public sector faces significant challenges with respect to data governance. At Infotel, we seamlessly integrate our core principles of data governance with customised software development and maintenance.
We build and maintain software solutions with embedded data governance frameworks, ensuring compliance with data privacy laws and secure handling of sensitive data. Also, our expertise with legacy modernization helps to align with current data governance trends, enabling secure data storage, access, and usage.
With our robust data governance solutions, Infotel demonstrates its commitment to supporting public sectors and enterprises in navigating the complexities of data management and compliance. By integrating innovative tools and strategies, we enable organisations to unlock the full potential of their data while maintaining the highest standards of security and accountability.
 Infotel, là où vous êtes
Infotel, là où vous êtes
