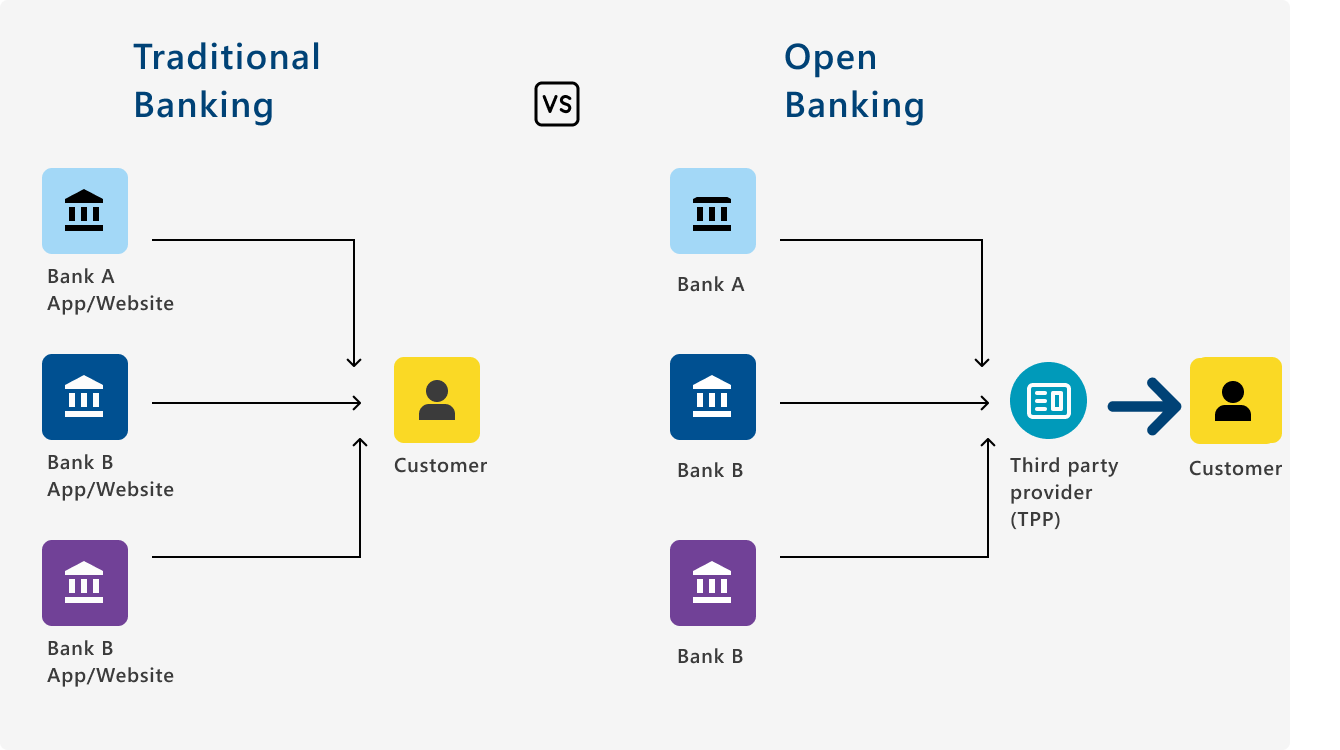
Introduction to Open Banking
Open Banking is a financial services model that allows third-party service providers to access consumer data from traditional banking systems through application programming interfaces (APIs). Open Banking gives more control to consumers over their financial information and offers new services and applications. Open Banking allows businesses to gain access to real-time financial data, optimise banking products, streamline payment services, and enhance customer account management.
The 2023 Juniper Research report predicts that the global value of open banking payment transactions will surpass $330 billion by 2027.
With the evolving open banking initiatives and compliance requirements, such as PSD2 (Payment Services Directive) in the European Union, businesses are using open banking to provide customers with more secure, efficient, and personalised financial experiences.
The APIs in open banking are broadly classified into three main categories:
- Data APIs: They provide read-only access to account information, balances, and transaction history.
- Transaction APIs: They enable fund transfers, direct debits, and payment services.
- Product APIs: The product APIs allow third parties to list financial products, rates, and terms.
Benefits of Open Banking for Businesses
Open banking enables businesses to access the financial data of customers with their consent, allowing them to offer more personalised and better products and services.
Open banking allows businesses to automate and streamline their financial processes, including accounting and compliance.
- Open banking helps businesses tap into new sources of financing, increasing their revenue.
- Improves customer experience by helping businesses to detect and prevent fraud.

Open Banking is reshaping financial services—from secure API integration to real-time data access.
At Infotel, we help banks and fintechs go beyond compliance to unlock agility, trust, and innovation
Features of Open Banking

Open Banking has the potential to create revenue-sharing ecosystems where customers are given access to third-party apps and incumbents’ profits on a subscription or referral basis.
Account Information Services (AIS)
It enables consumers to share their financial data securely with authorised third parties, fostering innovation in personal finance management. This not only enhances financial transparency but also empowers customers to make informed decisions about their finances.
This includes their transaction history, retrieving account balances, etc. Account Information Services APIs enable developers to build applications that provide a consolidated view of the customers’ financial information across multiple banks.
Payment Initiation Services (PIS)
Payment Initiation Services (PIS) APIs enable third-party providers to initiate payments on behalf of customers where the payments are done directly from their bank accounts to recipients, bypassing the need for traditional payment methods. PIS APIs also facilitate real-time fund transfers that include both domestic and cross-border payments.
Funds Confirmation
Funds confirmation APIs allow third-party providers to check the availability of funds in a customer’s account before initiating a payment. This feature helps mitigate the risk of insufficient funds and provides real-time confirmation, ensuring successful and efficient transactions.
Consent Management
Open banking APIs include consent management capabilities, allowing customers to permit and revoke access permissions to their financial data. It enables customers to control which third-party providers can access their account information or initiate payments on their behalf. The Consent Management feature enhances data privacy and provides customers greater control over their financial information.
Strong Authentication and Security
Modern open banking APIs prioritize strong authentication and security measures to protect sensitive financial information. These APIs typically require two-factor authentication (2FA), OAuth-based authorization mechanisms, and encrypted communication protocols (such as HTTPS) to ensure secure data transmission.
Regulatory Compliance
Open banking APIs adhere to regulatory frameworks, such as the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) in the European Union. Compliance features ensure that customer data is protected, consent management is in place, and security standards are met. APIs often incorporate features like strong customer authentication (SCA) and transaction monitoring to comply with regulatory requirements.
Open Banking Evolution in Europe
- Europe is the dominant player in the global open banking market, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.8% between 2023 and 2031.
- Some of the key open banking segments in Europe include banking and capital markets, payments, digital currencies, and value-added services.
- The largest segments are banking and capital markets, while payments is the fastest-growing segment.
Open Banking Evolution in the Middle East
In the UAE, Emirates NBD Bank launched its API Sandbox in 2018, becoming the first bank in the UAE to enable open banking collaboration. In 2023, the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE) introduced the Financial Infrastructure Transformation (FIT) Programme, aiming to accelerate digital transformation in financial services. The UAE continues to lead in digital finance, with open banking initiatives supporting greater financial inclusion and cross-border fintech collaboration.
Saudi Arabia: Inspired by the UK, the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) published its inaugural Open Banking Framework in November 2022. This framework mandates that banks make their account information APIs available. The initial focus was on account information services (AIS), which centred on enabling the secure sharing of banking data.
Bahrain: As one of the first movers in the region, Bahrain has already implemented open banking regulations and is now refining its frameworks to support open finance.
Open Banking in India
Open banking in India has progressed from traditional banking silos to a dynamic, API-driven ecosystem. The journey began in 2016 with the launch of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), revolutionising digital transactions. This was followed by the development of India Stack, a set of digital public goods including Aadhaar, e-KYC, and e-Sign, which laid the groundwork for secure, consent-based data sharing. The Account Aggregator (AA) framework and Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA) further enabled individuals to control and share their financial data across institutions. Unlike Western models that are either market- or regulation-driven, India’s approach blends both, promoting innovation while ensuring data privacy through the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act.
From Liability to Asset: Transforming Dark Data for Open Banking Compliance
‘Dark data’ refers to the vast volumes of unstructured, unused, or forgotten information that organisations collect but do not actively analyse. The types of dark data are legacy customer records, transaction logs, call centre transcripts, and outdated KYC documents. In the context of open banking, where secure data sharing and transparency are critical, dark data becomes a liability if left unmanaged. As per the 2022 report from Enterprise Strategy Group, 47% of all data is dark data, on average, with a fifth of respondents saying more than 70% of their data is dark data.

Risks of dark data in Open Banking include:
-
The unaccounted-for sensitive data can lead to regulatory non-compliance, such as GDPR and RBI.
-
Security vulnerabilities from unmonitored data stores.
-
Operational inefficiencies caused by redundant or conflicting data across APIs and partner systems.
How Infotel’s Data Remediation Services Help
Infotel’s structured data remediation framework is purpose-built for financial institutions navigating open banking transformation:
Discovery & Classification of data
Identify dark data from both structured and unstructured sources.
Classify sensitive, redundant, or obsolete data (e.g., PII, financial records)
Cleansing & Consolidation
Remove duplicates, correct inconsistencies, and enrich incomplete records.
Align data formats for API-readiness and partner interoperability
Cleansing & Consolidation
Ensure data aligns with regulatory mandates (e.g., consent, retention policies).
Enable audit trails and data lineage for transparency.
Activation & Value Extraction
Transform dark data into actionable insights for credit risk, customer segmentation, and fraud analytics
Improve API performance and reduce latency by eliminating data clutter.
Business Impact of Dark Data Remediation in Open Banking Ecosystems
Infotel’s structured data remediation framework is purpose-built for financial institutions navigating open banking transformation:
- Faster partner onboarding with clean, standardised datasets.
- Eliminates redundant, obsolete, or conflicting data across systems
- Strengthens compliance with GDPR, RBI, PSD2, and consent-driven data sharing norms.
- Enhanced customer trust via secure, consent-driven data sharing.
- Improved analytics for personalised financial services and cross-sell opportunities.
Open banking marks a transformative shift in financial services, one that prioritises transparency, interoperability, and customer-centric innovation. By enabling secure data sharing through APIs, it has unlocked new possibilities for personalisation, competition, and financial inclusion.
 Infotel, là où vous êtes
Infotel, là où vous êtes

